Introduction
The healthcare sector is undergoing a profound transformation driven by technological advancements. Among the most significant innovations are artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics, which are reshaping patient care and revolutionizing medical practices. From diagnostic tools to surgical procedures, these technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. This essay explores the impact of AI and robotics on healthcare, highlighting key innovations, current applications, and future possibilities.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
1. AI-Powered Diagnostics
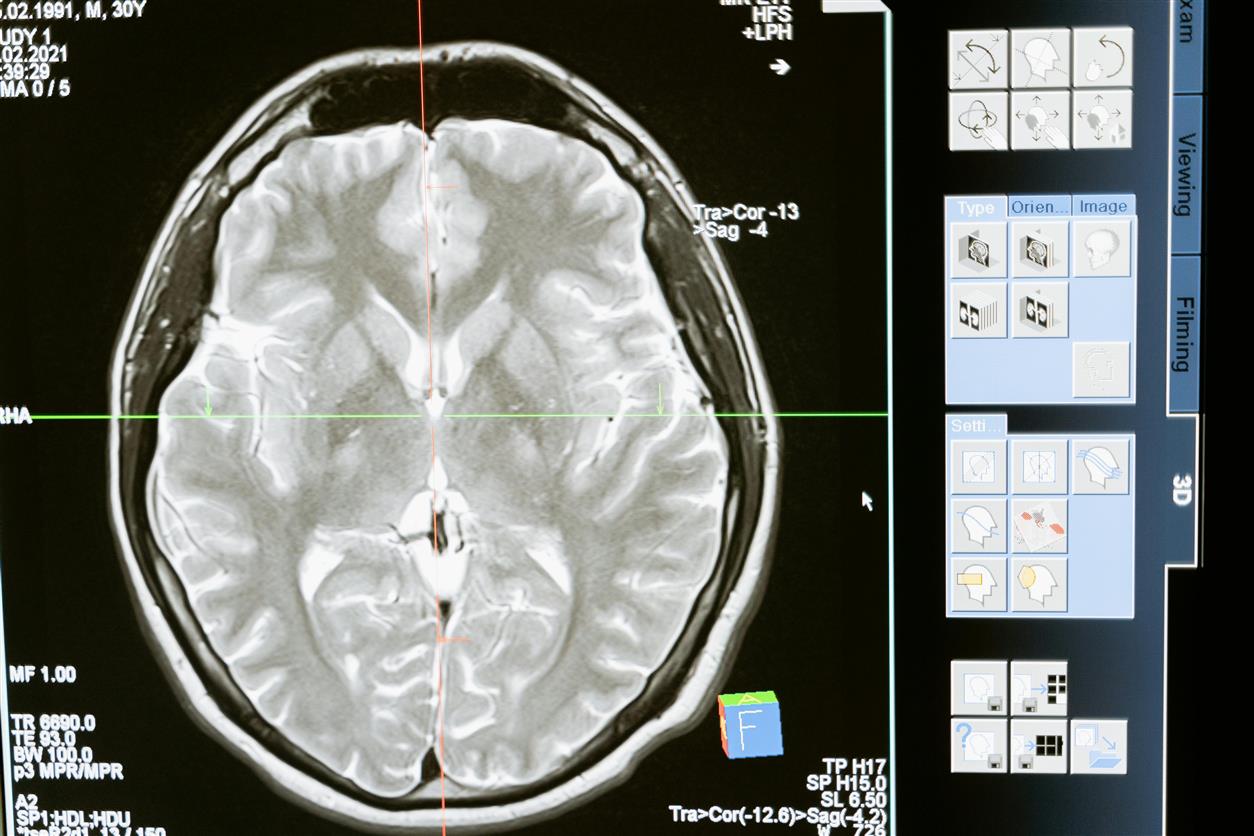
Artificial intelligence is making strides in diagnostics, offering tools that analyze medical images, detect anomalies, and support clinical decision-making. AI algorithms, particularly those based on deep learning, are trained to recognize patterns in large datasets, enabling them to assist in diagnosing a range of conditions from cancers to neurological disorders.
Examples of AI in Diagnostics:
- Radiology: AI systems analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify abnormalities such as tumors or fractures. For instance, Google’s DeepMind has developed AI models that outperform radiologists in detecting eye diseases and cancers.
- Pathology: AI tools assist pathologists in examining tissue samples, enhancing accuracy in diagnosing diseases like cancer by identifying subtle patterns that might be missed by human eyes.
Benefits of AI Diagnostics:
- Increased Accuracy: AI can reduce diagnostic errors and improve the precision of disease detection.
- Early Detection: AI algorithms can identify conditions at earlier stages, leading to timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
- Efficiency: Automation of diagnostic tasks can streamline workflows, reducing the burden on healthcare professionals and accelerating patient care.
2. Personalized Medicine
AI is pivotal in the development of personalized medicine, which tailors treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health data. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can identify patterns and correlations that inform personalized treatment plans.
Applications of Personalized Medicine:
- Genomic Analysis: AI algorithms analyze genomic data to identify genetic mutations associated with diseases, guiding targeted therapies.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models predict individual responses to treatments, allowing for customized drug regimens and reducing adverse effects.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine:
- Optimized Treatments: Patients receive treatments specifically suited to their genetic profiles and health conditions.
- Reduced Side Effects: Tailored therapies minimize the risk of adverse reactions and improve overall effectiveness.
- Enhanced Outcomes: Personalized approaches lead to more effective and efficient treatment strategies.
3. AI in Patient Monitoring and Management
AI technologies are enhancing patient monitoring and management by analyzing real-time data from wearable devices and health records. This continuous monitoring enables proactive care and timely interventions.
Examples of AI in Monitoring:
- Wearables: AI-driven wearable devices track vital signs such as heart rate, blood glucose levels, and activity, alerting patients and healthcare providers to potential issues.
- Remote Monitoring: AI platforms analyze data from remote monitoring systems to manage chronic conditions, adjusting treatment plans as needed and reducing hospital visits.
Benefits of AI in Patient Monitoring:
- Continuous Surveillance: Real-time monitoring provides constant oversight of patient health, leading to early detection of problems.
- Proactive Care: AI-driven alerts enable timely interventions, improving patient management and reducing emergency situations.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI analysis of large datasets offers valuable insights into patient health trends and treatment effectiveness.
The Impact of Robotics on Healthcare
1. Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery has transformed surgical procedures, offering precision, control, and minimally invasive techniques that improve patient outcomes. Surgical robots enhance the surgeon’s ability to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and reduced recovery times.
Examples of Robotic-Assisted Surgery:
- Da Vinci Surgical System: This widely used system allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive surgeries with high precision, including prostatectomies and hysterectomies.
- Robo-Assistive Devices: Robots such as the RAS (Robot-Assisted Surgery) systems assist in orthopedic surgeries, spinal procedures, and other complex operations.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Surgery:
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions lead to reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times.
- Enhanced Precision: Robotic systems provide greater dexterity and precision, improving surgical outcomes.
- Reduced Complications: Lower risk of surgical complications and infections due to minimally invasive techniques.
2. Robotic Rehabilitation and Therapy
Robotic technology is revolutionizing rehabilitation and therapy by providing patients with customized and intensive therapeutic interventions. Robotic rehabilitation devices assist patients in regaining motor function and mobility.
Examples of Robotic Rehabilitation:
- Exoskeletons: Wearable robotic exoskeletons support patients with mobility impairments, aiding in walking and physical therapy.
- Robotic Physical Therapy: Robotic devices guide patients through exercises, providing consistent and precise movements to improve motor skills and strength.
Benefits of Robotic Rehabilitation:
- Enhanced Recovery: Robotic devices offer targeted and repetitive therapy, accelerating recovery and improving outcomes.
- Customized Therapy: Robots adjust therapy based on individual patient needs and progress.
- Increased Motivation: Interactive and engaging robotic therapies enhance patient motivation and adherence to rehabilitation programs.
3. Robotic Assistance in Patient Care
Robots are increasingly used to assist in patient care tasks, ranging from routine activities to complex procedures. These robots can provide support in hospitals, nursing homes, and home care settings.
Examples of Robotic Assistance:
- Hospital Robots: Robots assist with tasks such as delivering medication, transporting supplies, and performing routine cleaning duties.
- Companion Robots: Robots like Paro provide companionship and emotional support to elderly patients, improving their well-being.
Benefits of Robotic Assistance:
- Improved Efficiency: Robots streamline repetitive tasks, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on more critical aspects of care.
- Enhanced Patient Interaction: Companion robots offer emotional support and social interaction, benefiting patients’ mental health.
- Reduced Strain: Robots reduce physical strain on healthcare workers by handling physically demanding tasks.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The integration of AI and robotics in healthcare raises ethical and privacy concerns. Ensuring that patient data is protected and used responsibly is paramount. Additionally, ethical considerations surrounding AI decision-making and robotic autonomy must be addressed.
Key Ethical and Privacy Concerns:
- Data Security: Protecting patient data from breaches and unauthorized access is essential.
- Bias in AI: Addressing potential biases in AI algorithms to ensure fair and equitable care.
- Autonomy and Consent: Ensuring that patients are informed and consent to the use of AI and robotics in their care.
2. Cost and Accessibility
While AI and robotics offer significant benefits, the cost of implementing these technologies can be prohibitive for some healthcare facilities. Ensuring that advancements are accessible to a broader range of healthcare providers and patients is crucial.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations:
- High Costs: The expense of acquiring and maintaining AI and robotic systems can be a barrier for smaller healthcare providers.
- Training Requirements: Adequate training for healthcare professionals is necessary to effectively utilize new technologies.
- Equitable Access: Ensuring that advancements are accessible to underserved and rural areas.
3. Integration and Interoperability
Integrating AI and robotic systems into existing healthcare infrastructure can be challenging. Ensuring interoperability with other systems and workflows is critical for maximizing the benefits of these technologies.
Integration Considerations:
- System Compatibility: Ensuring that new technologies integrate seamlessly with existing electronic health records (EHR) and medical devices.
- Workflow Integration: Adapting workflows to incorporate AI and robotics without disrupting patient care.
- Interoperability Standards: Adhering to standards that facilitate communication and data exchange between different systems.
Future Directions
1. Advancements in AI and Robotics
Future developments in AI and robotics will continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in healthcare. Innovations such as advanced machine learning algorithms, more sophisticated robotic systems, and enhanced human-robot interaction are expected to further transform patient care.
Emerging Trends:
- AI in Precision Medicine: Advancements in AI will enable even more precise and personalized treatment options.
- Robotic Innovations: Future robots may offer even greater dexterity, functionality, and adaptability for various medical applications.
- Integration of AI and Robotics: The convergence of AI and robotics will lead to new applications and capabilities in patient care.
2. Expansion of Telemedicine
The integration of AI and robotics will play a significant role in expanding telemedicine capabilities. Remote consultations, robotic-assisted procedures, and AI-driven diagnostics will enhance the accessibility and quality of care for patients in remote or underserved areas.
Telemedicine Developments:
- Remote Robotic Surgery: Enabling surgeons to perform procedures remotely using robotic systems.
- AI-Enhanced Telehealth: Leveraging AI to analyze data and provide real-time insights during remote consultations.
3. Collaboration and Research
Collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and researchers will be essential for advancing AI and robotics in healthcare. Ongoing research and innovation will drive the development of new technologies and applications.
Future Collaborations:
- Interdisciplinary Research: Combining expertise from AI, robotics, and healthcare to develop cutting-edge solutions.
- Clinical Trials: Conducting trials to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of new technologies in real-world settings.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with technology companies and academic institutions to accelerate innovation and implementation.

Conclusion
Technological innovations in artificial intelligence and robotics are profoundly transforming patient care and the healthcare industry as a whole. AI-powered diagnostics, personalized medicine, and patient monitoring are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of medical care. Meanwhile, robotics are revolutionizing surgical procedures, rehabilitation, and patient assistance, improving outcomes and quality of life.
As these technologies continue to evolve, addressing challenges related to ethics, cost, and integration will be crucial for maximizing their benefits. The future of healthcare promises even greater advancements, with ongoing research and collaboration driving innovation. By embracing these technologies and adapting to new developments, healthcare providers can enhance patient care, improve operational efficiency, and contribute to the ongoing transformation of the healthcare landscape.