Introduction
In the ever-changing landscape of finance and economics, interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping economic activity. Rising interest rates, in particular, have significant implications for various sectors, including housing and personal finance. For homebuyers and borrowers, the impact of increasing interest rates can be profound, influencing purchasing decisions, borrowing costs, and long-term financial planning. This essay explores the effects of rising interest rates on homebuyers and borrowers, examining how these changes can affect affordability, borrowing behavior, and overall financial stability. We will also discuss strategies for navigating a high-interest-rate environment and the potential long-term consequences for individuals and the broader economy.
Understanding Interest Rates
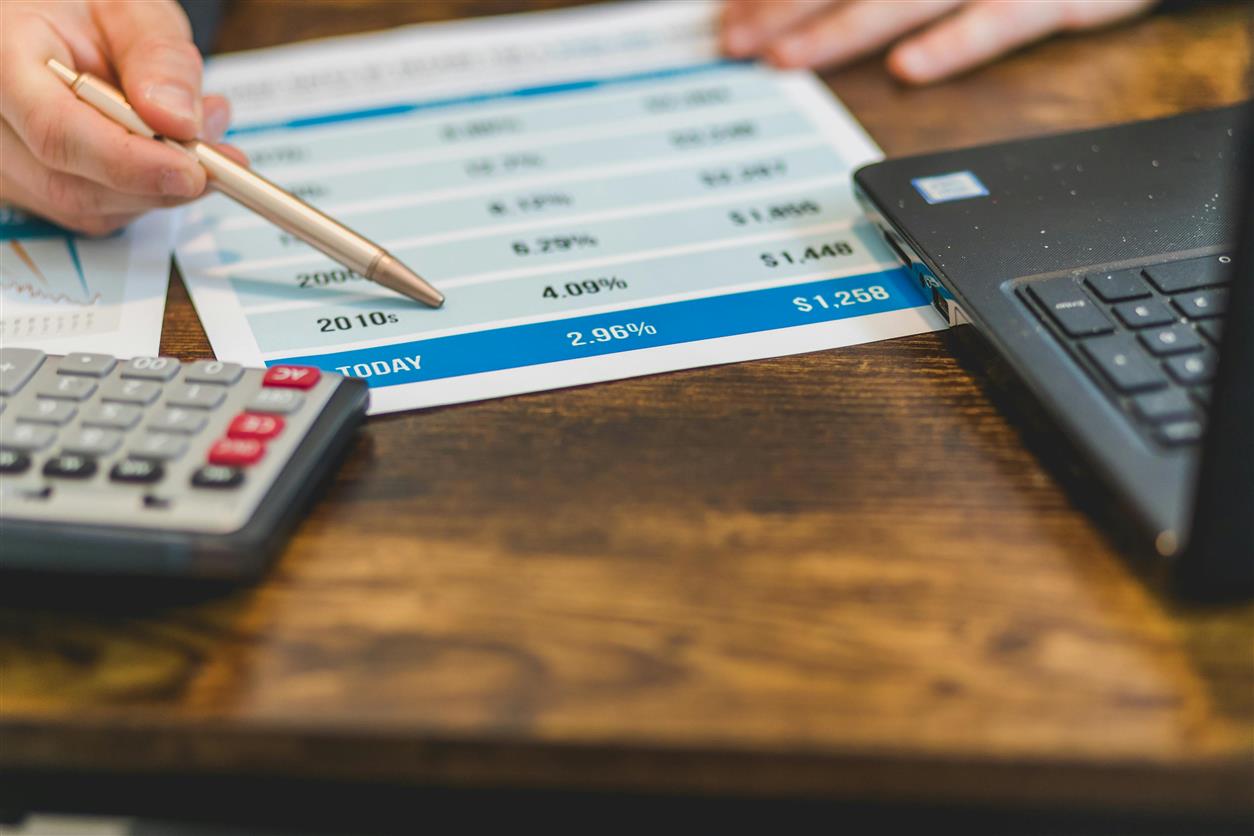
Definition and Mechanism: Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the principal amount. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, set benchmark interest rates, which influence the rates offered by banks and financial institutions. When central banks raise interest rates, borrowing costs increase, affecting various aspects of the economy.
Historical Context: Interest rates have fluctuated significantly over time due to economic conditions, inflation, and monetary policy decisions. Historically, periods of rising interest rates have often coincided with efforts to control inflation or stabilize economic growth. Understanding these historical patterns provides context for assessing the current impact of rising rates.
Recent Trends: In recent years, interest rates have been relatively low, contributing to a favorable borrowing environment. However, as central banks respond to economic pressures such as inflation or financial stability concerns, interest rates may rise. The recent trend of increasing interest rates has raised questions about its effects on homebuyers and borrowers.
Impact on Homebuyers
Affordability and Purchasing Power: Rising interest rates can significantly affect home affordability. As mortgage rates increase, the cost of borrowing for a home purchase rises, leading to higher monthly mortgage payments. For many prospective homebuyers, this can reduce purchasing power, limiting their ability to afford a home or necessitating adjustments to their budget.
Mortgage Rates and Monthly Payments: Mortgage rates directly impact monthly mortgage payments. As interest rates rise, the cost of financing a home increases, leading to higher monthly payments for borrowers. This can affect the affordability of homes and influence the decision-making process for prospective buyers.
Home Prices and Market Dynamics: Rising interest rates can influence home prices and market dynamics. Higher borrowing costs may reduce demand for homes, potentially leading to slower price growth or even declines in certain markets. Sellers may need to adjust their expectations, and buyers may find opportunities for better deals in a higher-rate environment.
First-Time Buyers and Down Payments: First-time homebuyers may be particularly affected by rising interest rates. Higher mortgage rates can strain budgets and make it more challenging to save for a down payment. Additionally, first-time buyers may face increased competition from experienced buyers who are better equipped to handle higher borrowing costs.
Long-Term Financial Planning: For homebuyers, long-term financial planning becomes crucial in a rising interest rate environment. Fixed-rate mortgages may offer stability, while adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) could become more expensive over time. Buyers need to carefully consider their options and plan for potential future rate changes.
Impact on Borrowers
Cost of Borrowing: Rising interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for various types of loans, including personal loans, auto loans, and credit cards. Borrowers will face higher interest charges on outstanding balances and new credit, affecting their overall financial burden.
Debt Servicing and Repayment: For existing borrowers with variable-rate loans, rising interest rates can lead to higher monthly payments and increased debt servicing costs. This can strain household budgets and affect financial stability, particularly for those with significant outstanding debt.
Refinancing and Loan Terms: As interest rates rise, the attractiveness of refinancing existing loans diminishes. Borrowers seeking to refinance may face higher rates, reducing the potential benefits of refinancing. Additionally, individuals looking to take out new loans will encounter higher borrowing costs, affecting their ability to secure favorable loan terms.
Consumer Spending and Savings: Higher borrowing costs can impact consumer spending and savings behavior. With increased debt servicing costs, borrowers may reduce discretionary spending or adjust their savings plans. This can affect overall economic activity and individual financial well-being.
Credit Availability and Lending Standards: Rising interest rates may influence credit availability and lending standards. Financial institutions may tighten lending criteria to manage risk, making it more challenging for some individuals to obtain credit. Borrowers may need to meet stricter requirements or offer higher creditworthiness to secure loans.
Strategies for Navigating Rising Interest Rates
Fixed-Rate Loans vs. Adjustable-Rate Loans: When interest rates are rising, opting for fixed-rate loans can provide stability and predictability in borrowing costs. Fixed-rate mortgages and loans offer a consistent interest rate over the life of the loan, protecting borrowers from future rate increases. Adjustable-rate loans, on the other hand, may become more expensive as rates rise, potentially impacting affordability.
Budgeting and Financial Planning: Effective budgeting and financial planning are essential in a rising interest rate environment. Homebuyers and borrowers should carefully assess their budgets, consider potential changes in borrowing costs, and plan for future rate increases. Building a financial cushion and managing debt responsibly can help mitigate the impact of higher rates.
Refinancing Considerations: For existing borrowers, refinancing decisions should be carefully evaluated in light of rising interest rates. While refinancing may offer benefits in certain situations, borrowers should weigh the potential costs and benefits. Timing and rate conditions should be considered to make informed refinancing decisions.
Exploring Alternative Financing Options: In a high-interest-rate environment, exploring alternative financing options may be beneficial. For example, individuals may consider government-backed loan programs, credit unions, or specialized lenders that offer competitive rates. Understanding available options can help borrowers find more favorable terms.
Maintaining a Strong Credit Profile: Maintaining a strong credit profile is crucial for securing favorable borrowing terms. A good credit score can help borrowers qualify for better rates and loan conditions. Paying down existing debt, managing credit responsibly, and addressing any credit issues can improve creditworthiness.
Long-Term Consequences and Outlook
Economic Impact: Rising interest rates have broader economic implications, including effects on economic growth and stability. Higher borrowing costs can influence consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity. Understanding these broader effects is important for assessing the long-term consequences of rising rates.
Housing Market Trends: The housing market may experience shifts in response to rising interest rates. Changes in demand, home prices, and market dynamics can impact both buyers and sellers. Monitoring housing market trends and adapting strategies accordingly can help individuals navigate the evolving real estate landscape.
Policy and Regulatory Responses: Governments and financial institutions may implement policy and regulatory measures to address the impact of rising interest rates. These measures may include adjustments to monetary policy, housing policies, and consumer protection regulations. Staying informed about policy changes can help individuals make informed financial decisions.
Future Projections: Looking ahead, interest rate trends and economic conditions will continue to influence borrowing and homebuying behavior. Monitoring economic indicators, central bank decisions, and market developments will provide insights into future rate changes and their potential impact.

Conclusion
Rising interest rates present significant challenges and opportunities for homebuyers and borrowers. The impact of higher borrowing costs on affordability, debt servicing, and financial planning underscores the importance of strategic decision-making in a high-interest-rate environment. By understanding the effects of rising rates, exploring effective strategies, and staying informed about market trends, individuals can navigate the complexities of borrowing and homebuying with greater confidence.
As the financial landscape evolves, adapting to rising interest rates requires careful consideration of loan options, budgeting practices, and long-term financial goals. By proactively managing borrowing costs and making informed decisions, homebuyers and borrowers can better navigate the challenges of a changing interest rate environment and work towards achieving their financial objectives.